
The first letter of alphabet is A and the first word in English that kids learn is, yes, no prizes for guessing- apple. That is how common apple is in our lives.
Apple is commercially the most important temperate fruit and is fourth among the most widely produced fruits in the world after banana, orange, and grape. China is the largest apple producing country in the world accounting for almost half (50%) of the world production. USA is the number 2 apple producer and India is among the top 5 apple producers.
In 1929, Russian scientist Nikolai Vavilov first traced the apple genome. He identified the primary ancestor of most cultivars of the domesticated apple to be the ancient apple tree: Malus sieversii. It has since been confirmed, through detailed DNA testing, and a full sequencing of the genome, as recently as 2010.
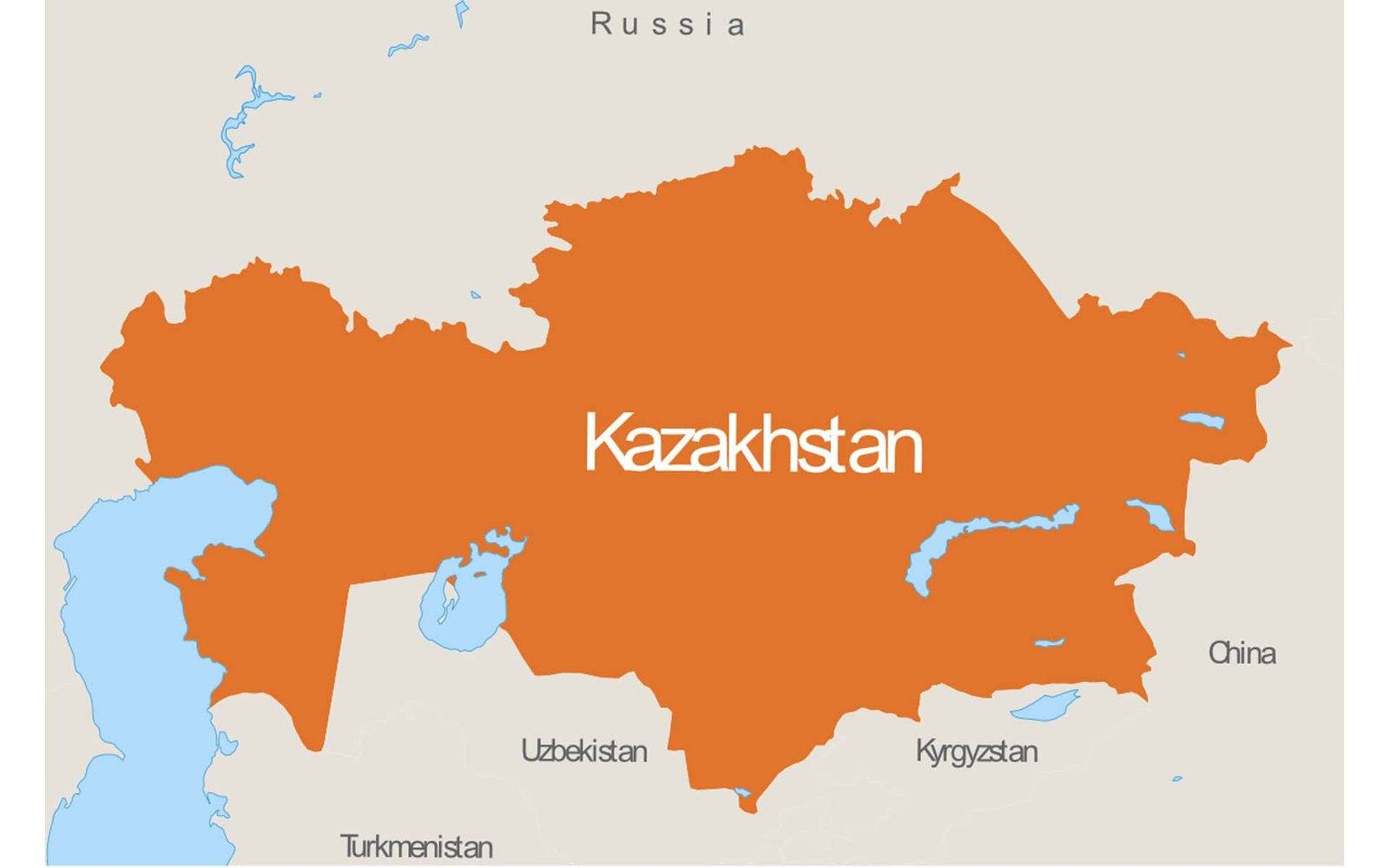
Malus sieversii is a wild apple, native to Central Asia, specifically to the Tian Shan Mountains of Kazakhstan, where they have been growing over millions of years and where they can still be found fruiting today. Kazakhstan’s city of Almaty, where these apple forests are found, was previously named as ‘Alma-Ata’ which translates from Kazakh as ‘Father of the Apples’.
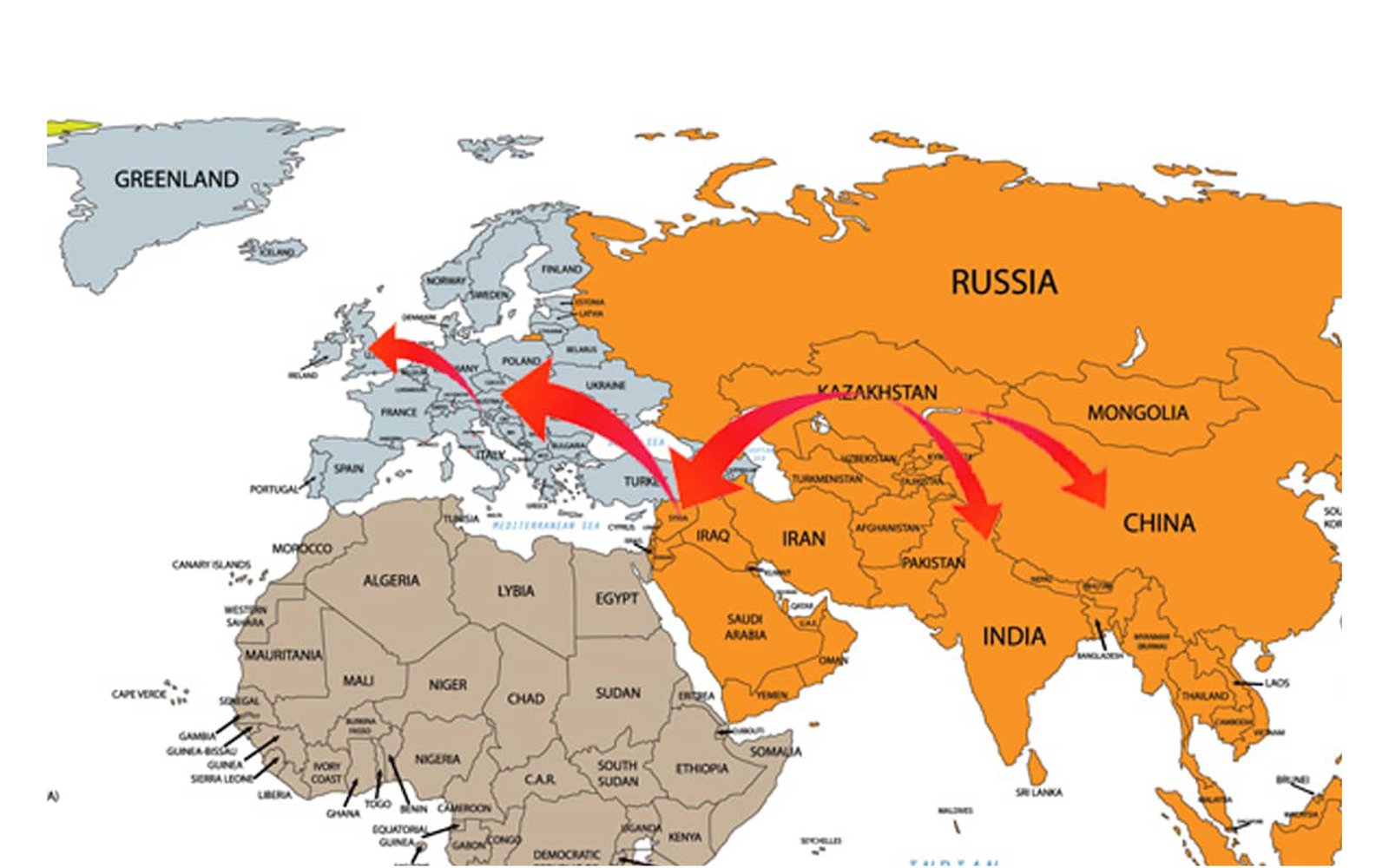
From Kazakhstan apples spread naturally to Syria, where the Romans picked them up and travelled along the Silk Road to bring them East. They learnt to graft and started to cultivate apples like the ones we know and enjoy today. Spreading across Europe to France, the fruit arrived in England at around the time of the Norman conquest in 1066.

The apple is a temperate fruit crop. Dry temperate climate is suitable for apple cultivation. The fruits produced in these areas are of high quality with high sugar content and long shelf life
Although apple growing areas in India do not fall in temperate zone, still the high-altitude Himalayan ranges ensure a temperate climate is maintained in the region.

Just 2 states of India, Jammu & Kashmir (now UTs), and Himachal account for 76% of the area under cultivation and almost 97% apple production. With Uttarakhand (2.5%) and Arunachal Pradesh (.3%) accounting for the remaining 3% production.
Volume wise J&K is the top apple grower by a large margin, producing 77% of total Indian apples compared to only 20% apples of Himachal Pradesh (almost 4 times!). In absolute terms J&K produces close to 1.8 million tons of apple, whereas Himachal Pradesh produces about half a million tons of apple.
India’s share in the total world apple production is merely 2.05%. Only around 1.6% of the country’s production gets exported.
| State | Apple Growing belts |
|---|---|
| Jammu & Kashmir | Srinagar, Budgam, Pulwama, Anatnag, Baramullah, Kupwara |
| Himachal Pradesh | Shimla, Kullu, Sirmour, Mandi, Chamba, Kinnaur |
| Uttaranchal | Almora, Pithoragarh, Tehri Garhwal, Uttarkashi, Chamoli, Dehradun, Nainital |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Tawang, West Kanneng, Lower Subansiri |
| Category | Varieties |
|---|---|
| Clonal rootstocks | M 9, M 26, M7, MM 106, MM 11 |
| Scab resistant | Prima, Priscilla, Sir Prize, Jonafree, Florina, Macfree, Nova Easy Grow, Coop 12, Coop 13 (Redfree), Nova Mac, Liberty, Freedom, Firdous, Shireen |
| Hybrids | Lal Ambri (Red Delicious x Ambri), Sunehari (Ambri x Golden Delicious), Chaubattia Princess, Chaubattia Anupam (Early Shanburry x Red Delicious), Ambred (Red Delicious x Ambri), Ambrich (Richared x Ambri), Ambroyal (Starking Delicious x Ambri) |
| Low Chilling | Michal, Schlomit, Anna, Tamma, Vered, Neomi, Tropical Beauty, Parlin’s Beauty |
| Pollinizing | Tydeman’s Early, Red Gold, Golden Delicious, Mc Intosh, Lord Lambourne, Winter Banana, Granny Smith, Starkspur Golden, Golden Spur |
Even though J&K is the largest producer of apple in India, Himachal Pradesh is called the 'Apple State'. There may be 2 reasons for it. Country's first apples were cultivated here, and apple is the most important crop of HP accounting for about 90% of the total horticultural production. Also, militancy is having a negative impact on overall economy of J&K including apple production & trade.
Though you will be amazed if you look at the data of value of apples rather than the quantity produced. Here, HP is easily close to the much larger producer J&K and in recent times it has even overtaken J&K by a margin. The superior price realization of HP apple says a lot about their quality. Superior quality may well be the third reason, which justifies the status of HP as the Apple State of India.

An Agri-export zone has been established in Himachal Pradesh covering the districts of Shimla, Sirmour, Kullu, Mandi, Chamba and Kinnaur considering the vast potential for increasing exports. Initial targets are for exporting apples to neighboring countries as well as to west Asia and to the south-east Asian countries.

With increase in production of apples in the HP, the state government is taking effective steps for its marketing besides providing packing material, transportation, ensuring adequate procurement of apples under Market Intervention Scheme, so that the growers get remunerative prices in the markets.
Arunachal Pradesh is one of the ideal locations for apple cultivation. If high yielding varieties of apple are introduced in the state it can make a big headway by exporting the produce to Bangladesh which presently depends on Bhutan besides meeting the internal demand of the northeastern markets.

For a common man apple can be eaten raw, can be juiced, and recently a fermented product apple cider vinegar is gaining popularity. Apple pies are yummy and a classic favorite. But that’s not all.

Apples and apple-based products are among the most popular foods around the world for their delightful flavors and health benefits. Apples are mostly consumed fresh, but a small part of the production is processed into juices, jellies, canned slices, and other items. If all you can think of is apple pie, see this long list which is prepared from apple.
Apple butter, Apple cake, Apple cheese, Apple chip, Apple cider, Apple cider vinegar, Apple crisp, Apple juice, Apple pie, Apple sauce, Apple seed oil, Apple strudel, Applejack, Baked apple, Calvados, Candy apple, Caramel apple, Cider, Ice cider, Jewish apple cake, Pectin
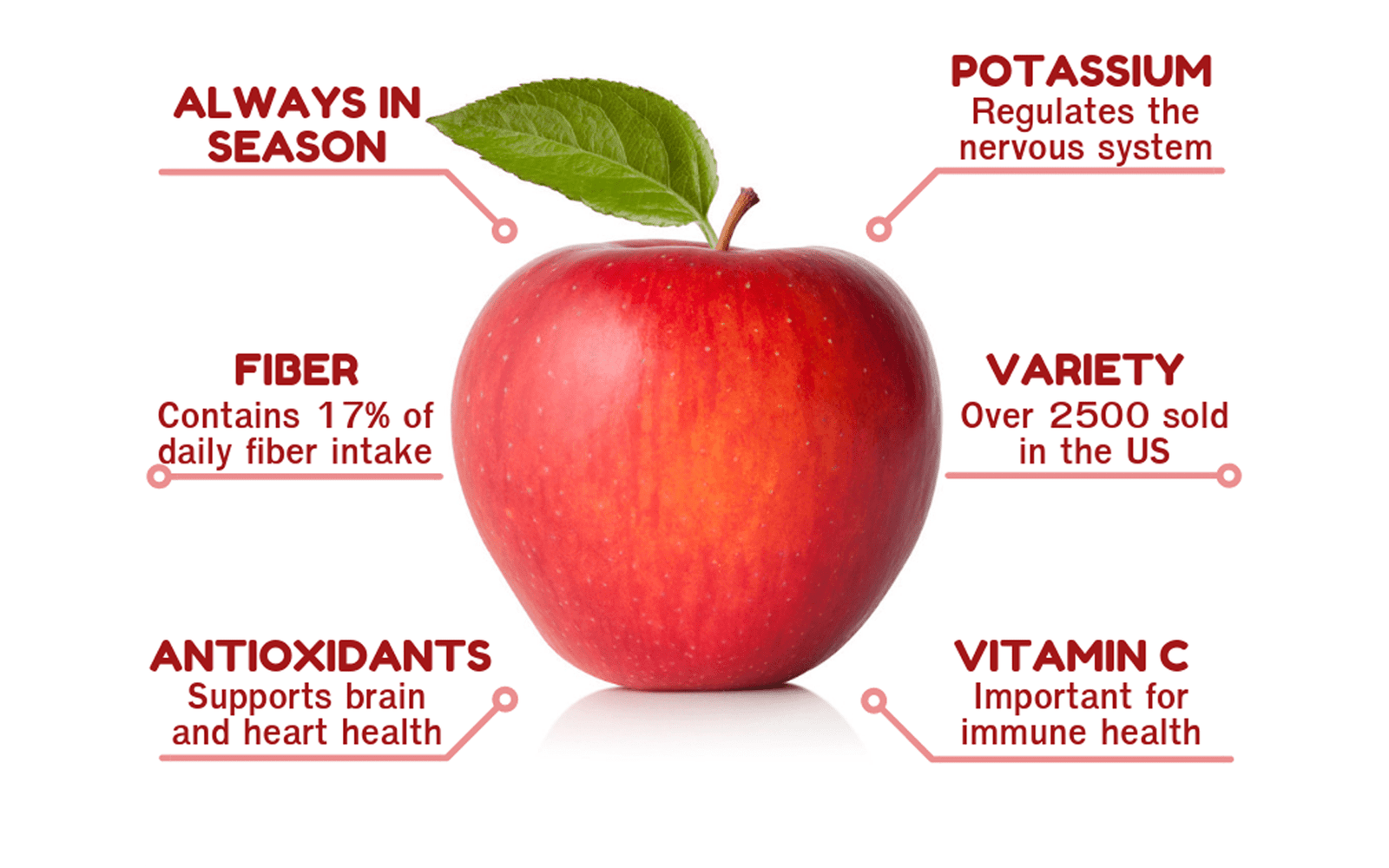
To Sum it Up
Apples are incredibly good for you and eating them is linked to a lower risk of many major diseases,
including diabetes and cancer. What’s more, its soluble fiber content may promote weight loss and gut
health. A medium apple equals 1.5 cups of fruit — which is 3/4 of the 2-cup daily recommendation for fruit.
For the greatest benefits, eat the whole fruit — both skin and flesh.

Table Apples: - Table apples or dessert apples are a group of apples grown for eating raw as opposed to cooking or cidermaking. These are usually sweet, and the most prized ones exhibit aroma variations that differentiate them from other apples.
Cooking Apples: - A cooking apple or culinary apple is an apple that is used primarily for cooking, as opposed to a dessert apple, which is eaten raw. Cooking apples are generally larger and can be tarter than dessert varieties.
Cider Apples: -Cider apples are a group of apples grown for their use in the production of cider. Cider apples are distinguished from "cookers" and "eaters", or dessert apples, by their bitterness or dryness of flavor, qualities which make the fruit unpalatable but can be useful in cidermaking.
Ornamental Apples: -Yes, you got it, there are few apple varieties which are grown for the way an apple tree looks!
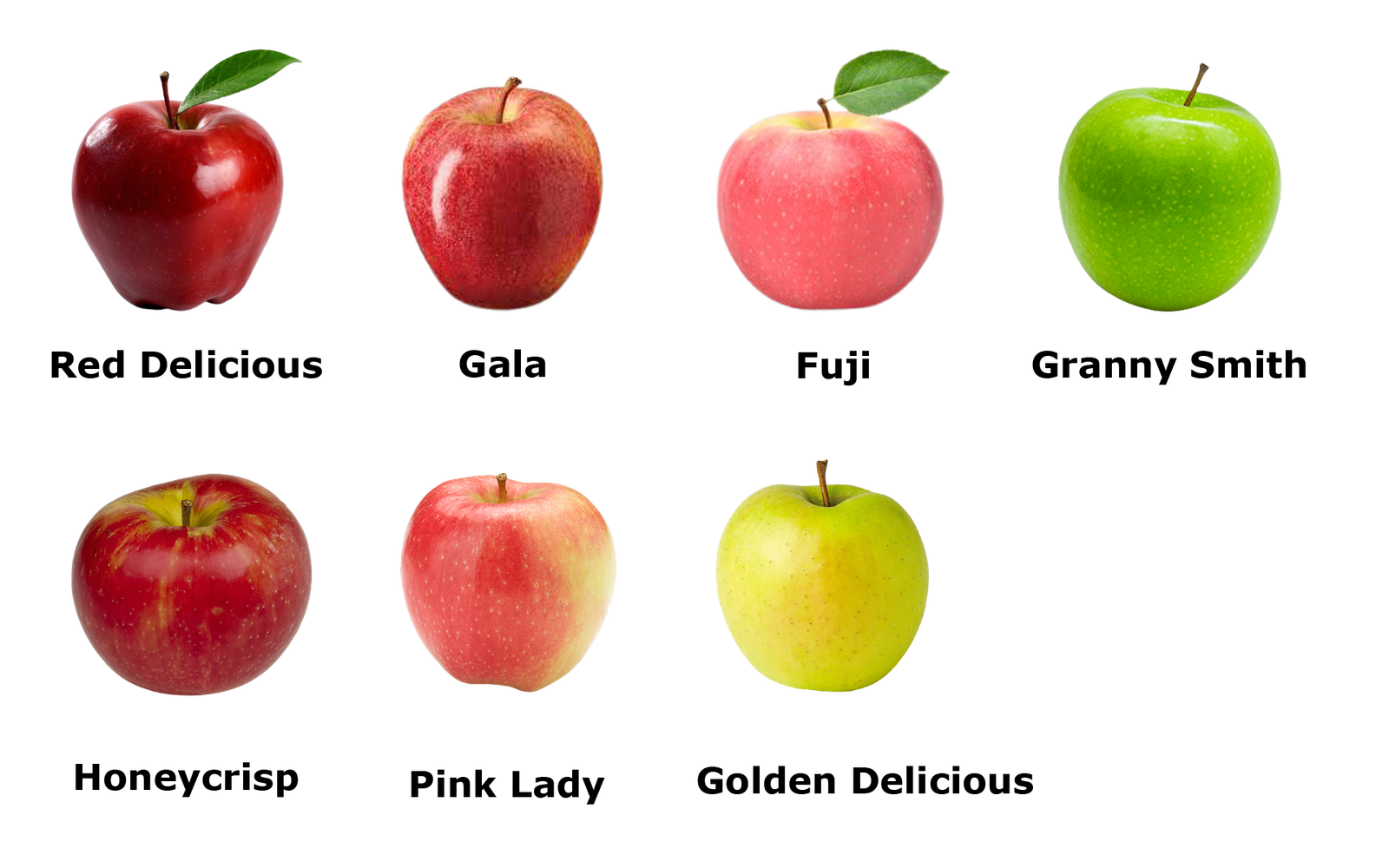

Fact: -Of the 30,000 apple varieties found all over the world only 30 are used and traded commercially

So much happens before the apple lands in your hand.
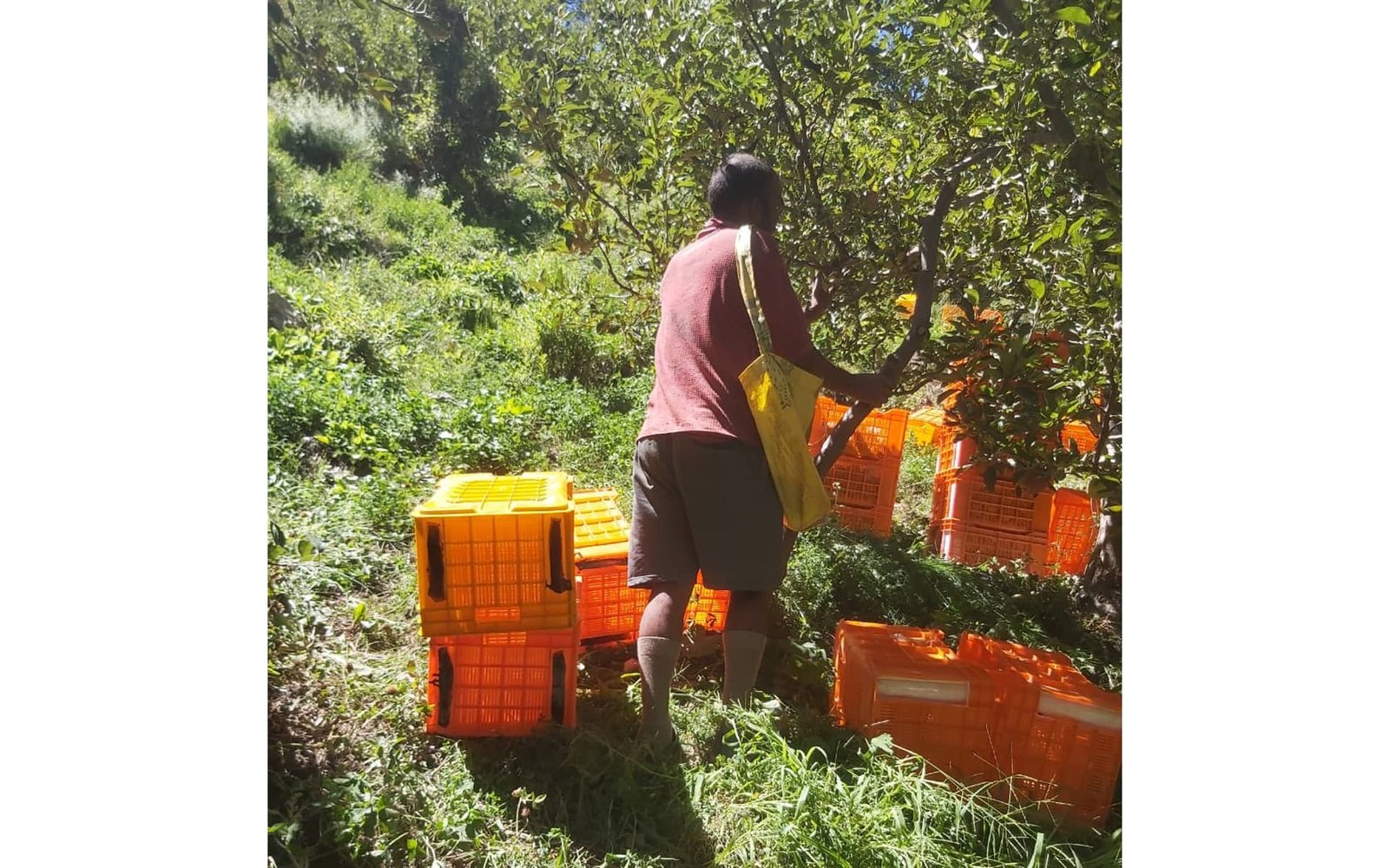

After all the hard work and all the stages, it is time to reap the crop. Normally the apples are ready for harvest from September-October except in the Nilgiris where the season is from April to July.
The fruits mature within 130-150 days after the full bloom stage depending upon the variety grown. The ripening of fruits is associated with the change in color, texture, quality, and the development of the characteristic flavor. Even though automation has started in apple picking in developed countries, in India it is still a totally manual process.
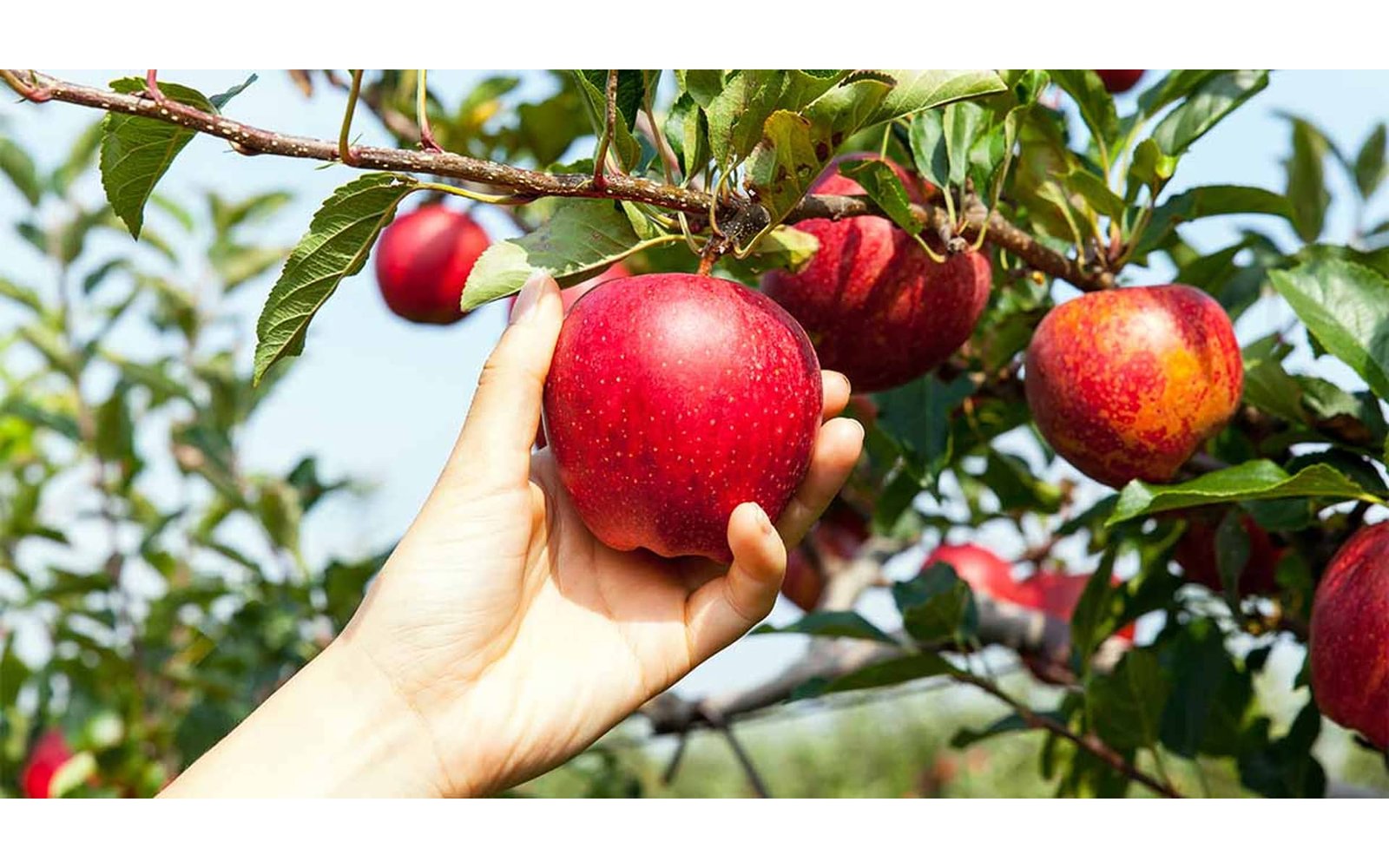

Fruit harvesting is a seasonal activity that occurs during harvest time in areas with fruit growing wild or being farmed in orchards.
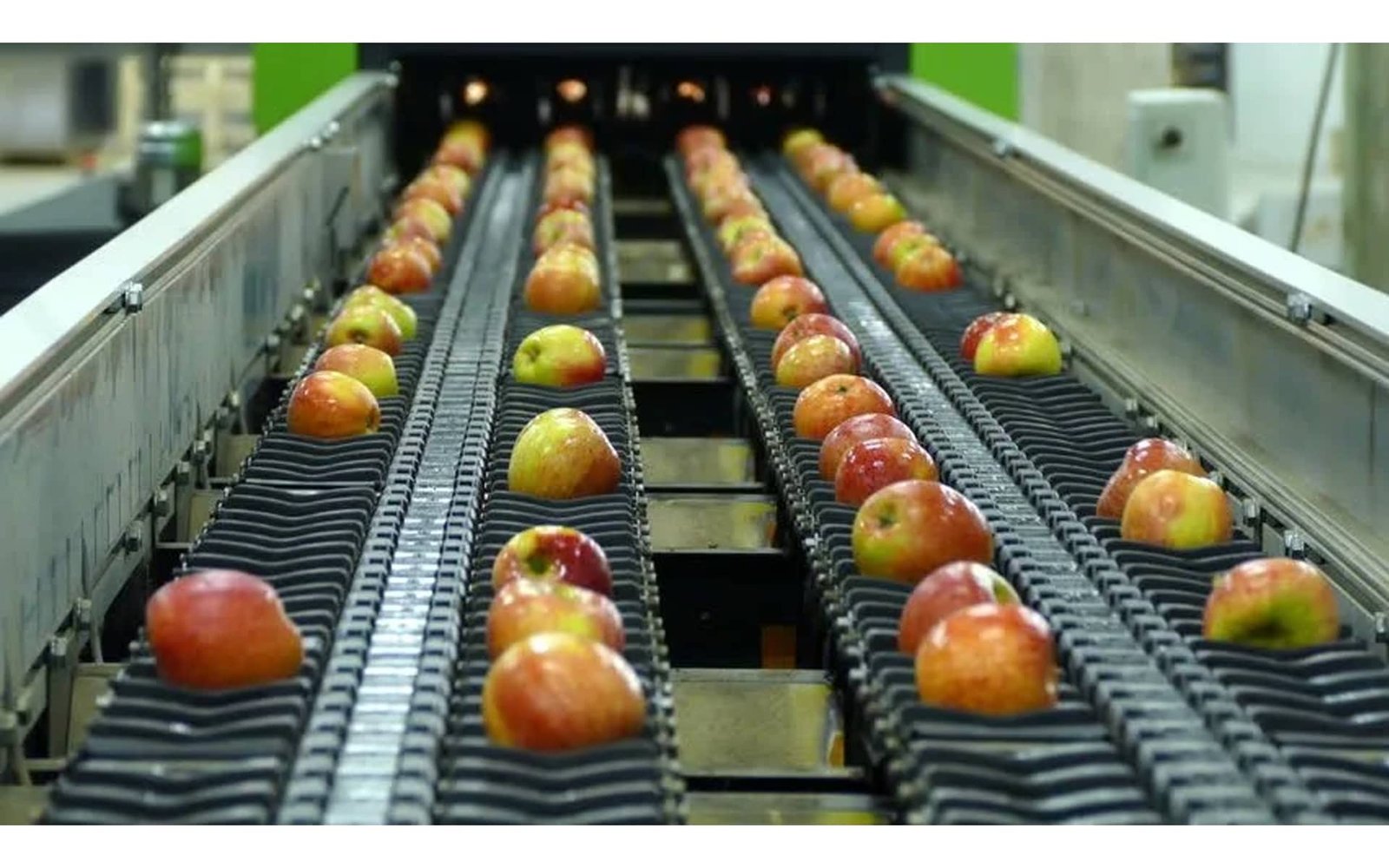

Grading of apples is done according to fruit size and fruit appearance or quality. Based on fruit size, apples are graded manually in 6 grades. Based on fruit color, shape, quality and appearance, apple fruits can be graded in three or more quality grades. These grades are designated as AAA, AA and A; A, B, C; or extra fancy, fancy class I and fancy class II.
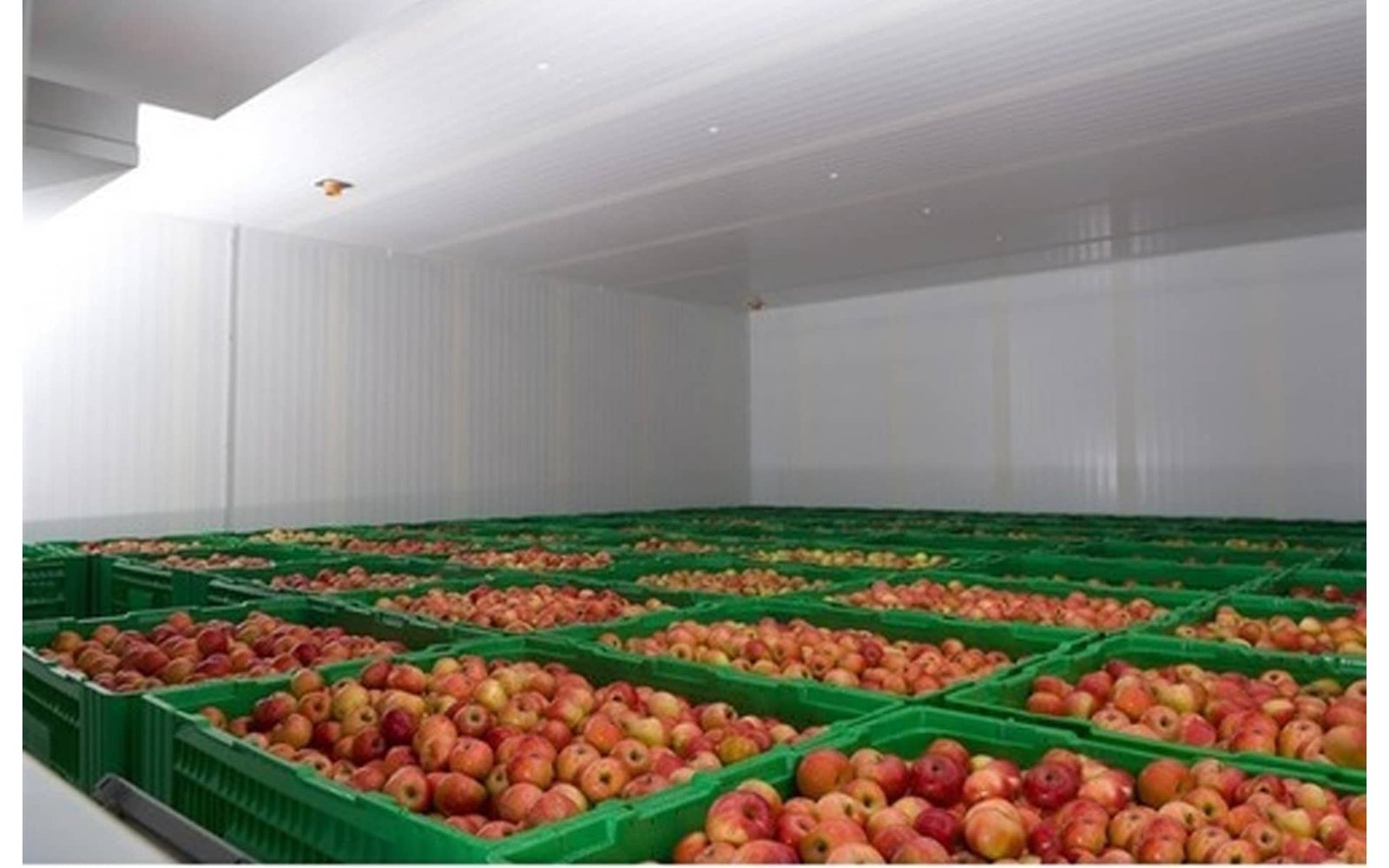

Apples have a long storage life compared to other fruits and can be stored for a period of 4-8 months after harvesting. The fruits can be kept in cold storage at a temperature of about – 1.10 C to 00 C and 85-90% relative humidity.
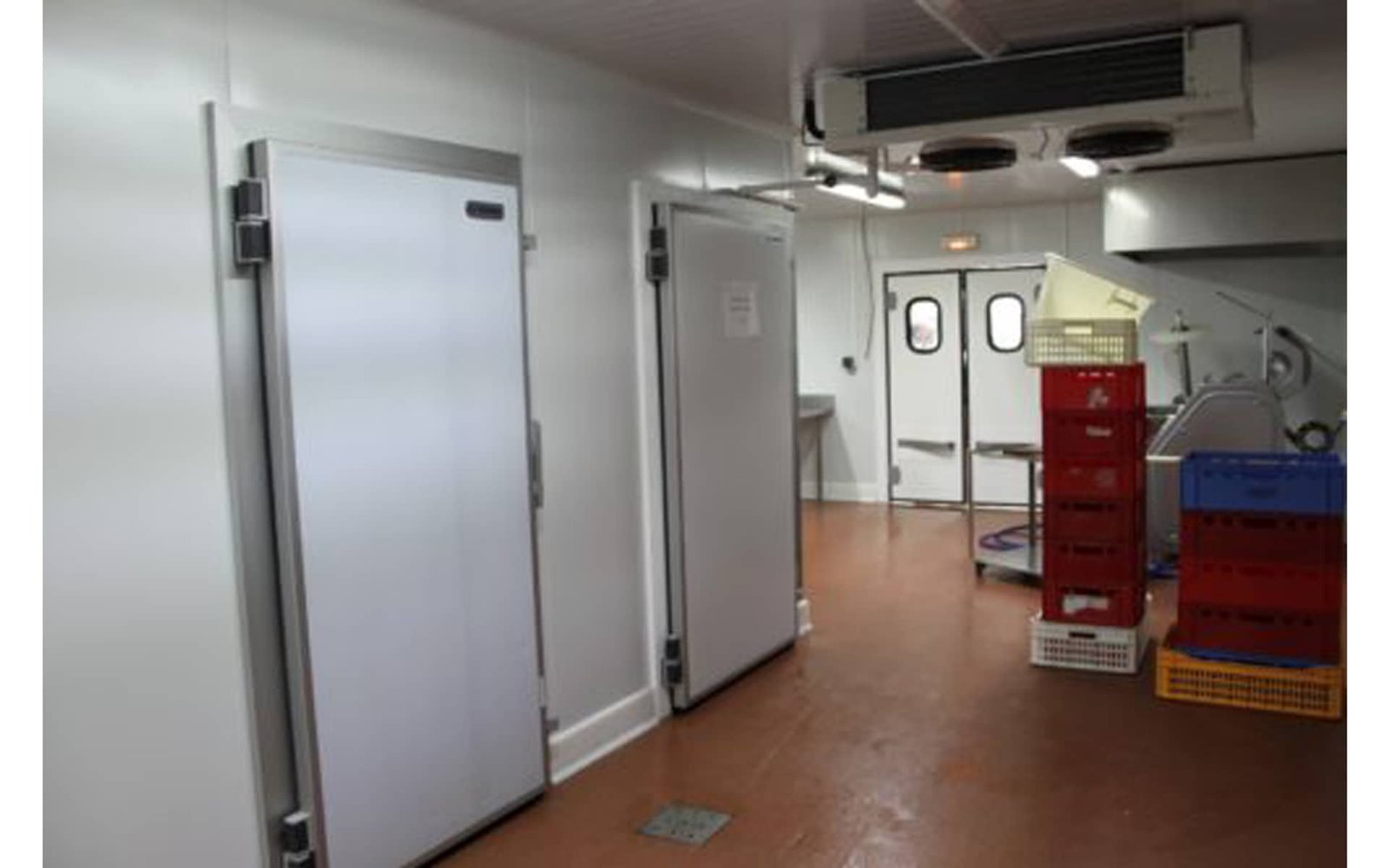

CA Storage involves carefully placing the apple in large airtight refrigerated rooms where temperature, oxygen, carbon-di-oxide, and humidity are carefully monitored. This controlled atmosphere slows down the respiration rate of the fruit which in turn slows the ripening process. Ripening slows down to the extent that the fruit can remain garden fresh, retaining full nutritional value almost till the next crop is ready.

A carton or box of apple is filled with homogenous (same grade- size as well as quality) apples. Kashmiri apples are usually packed in wooden boxes whereas Himachal Pradesh apples are predominantly packed using corrugated paper board cartons. Boxes come in 2 standard sizes. Half box having the capacity of about 10 kg. and full box that of 20 kg. fruit.
Apples are arranged in 5 rows in a large box (full box, weighing 20KG or more). Depending on size 80 to 175 apples (80, 100, 125, 150, 175) are packed in 5 rows. Very-small sized apples (pittu) are packed in 6 rows and a large box contains 240 apples. A smaller box (half box, containing 10KG or more) is generally used for packing only the best quality apples in 2 rows.
Many areas now have apple packing centers which uses a lot of automation in packing, minimizing the human handling.
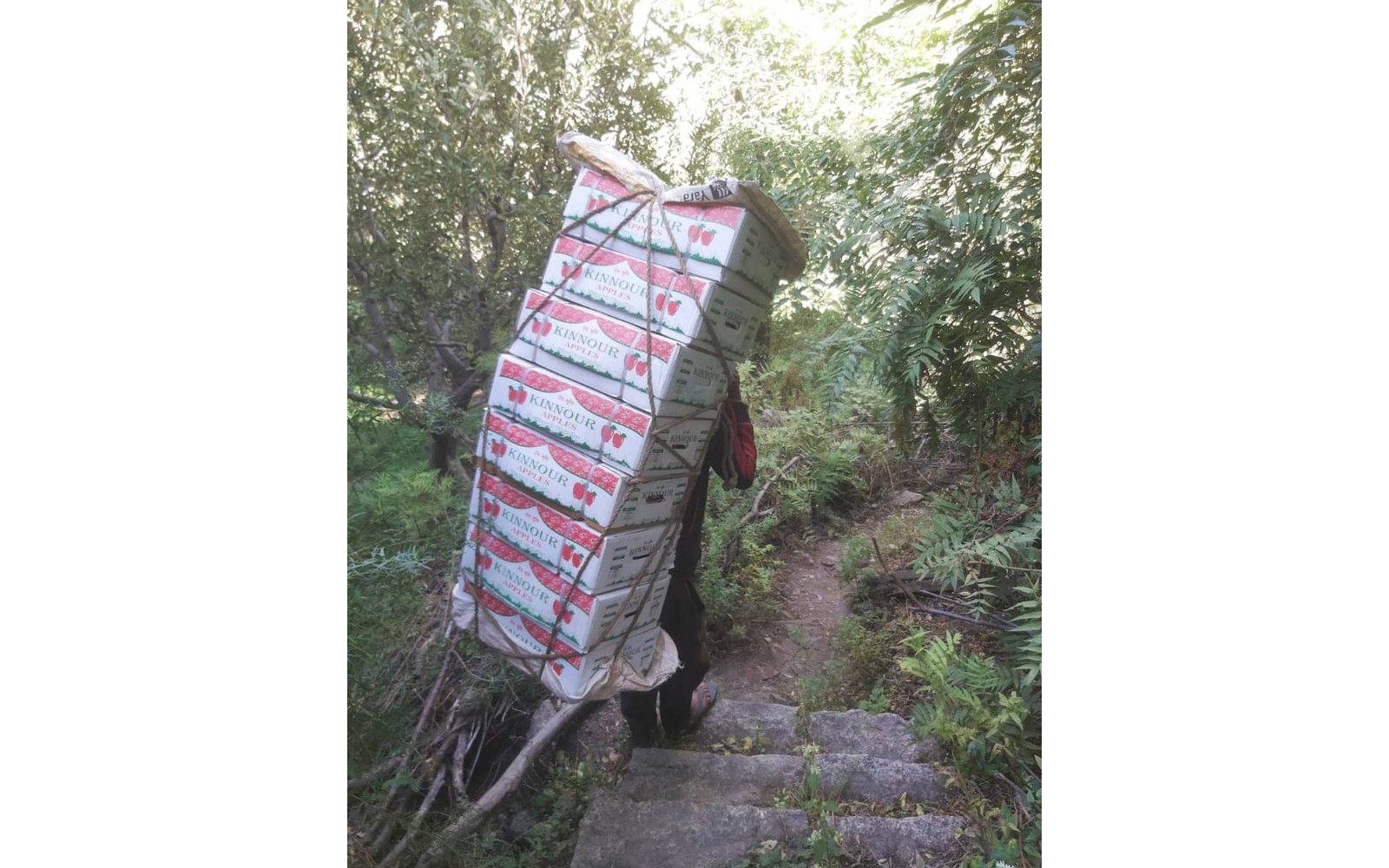

Road transport by trucks is the most popular mode of transport due to easy approach from orchards to the market. But since most of the orchards are far from the roads transporting the apples from orchards to grading and sorting centers and from there to loading points can be a task in itself- almost fully manual.

Himachal Pradesh is a state in the northern part of India. Situated in the Western Himalayas, it is one of the eleven mountain states and is characterized by an extreme landscape featuring several peaks and extensive river systems. Himachal Pradesh shares borders with Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Haryana, Uttarakhand, and Uttar Pradesh. The state shares an international border to the east with the Tibet Autonomous Region in China. The queen of hill stations Shimla is its capital.
Apple Growing Regions of Himachal Pradesh
Shimla, Kullu, Sirmour, Mandi, Chamba, Kinnaur
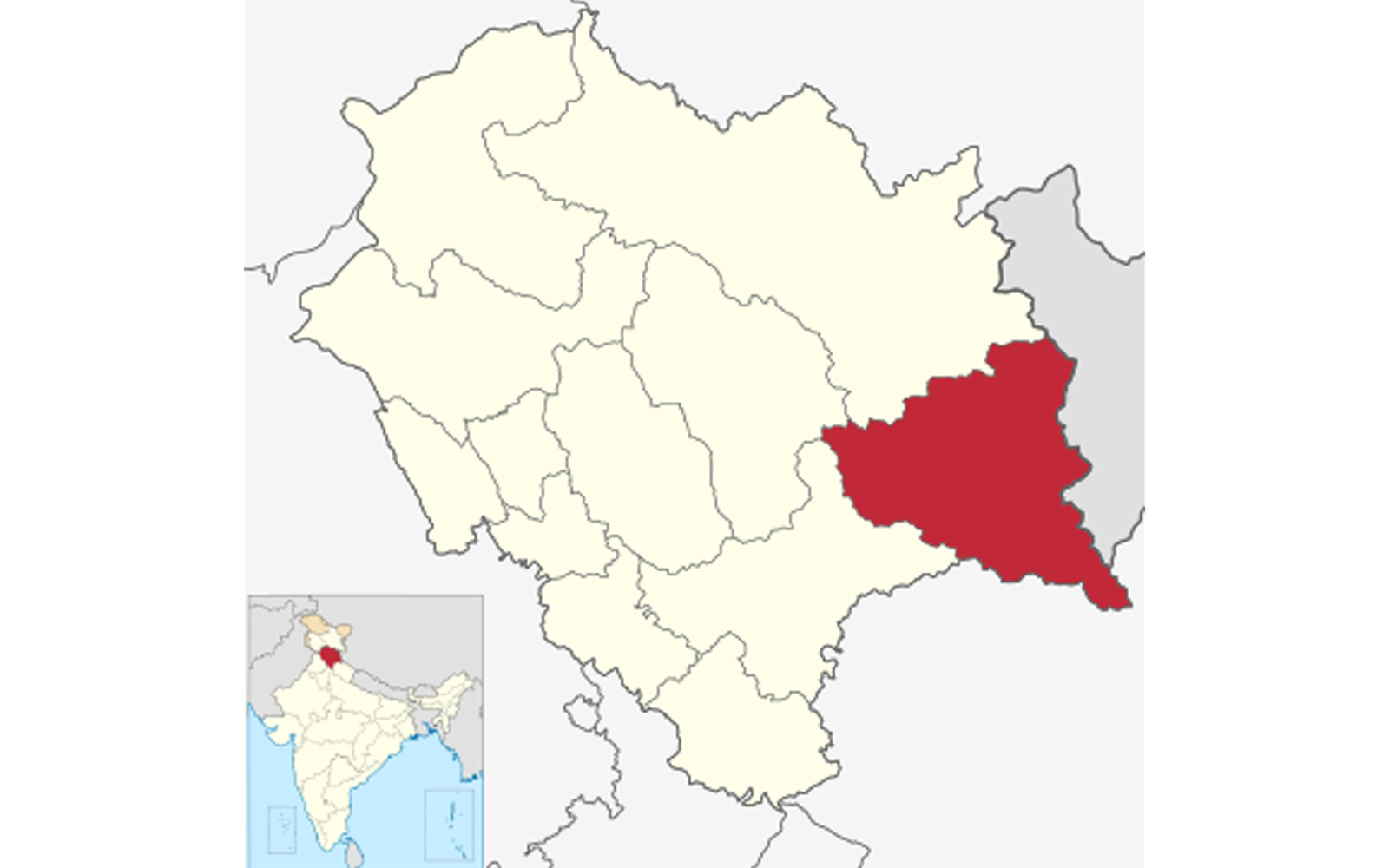
A mountainous area, ranging in altitude from 2,320 to 6,816 meters (7,612 to 22,362 ft), Kinnaur is one of the smallest districts in India by population. One of the twelve administrative districts of the state of Himachal Pradesh in northern India, it is about 235 km (146 mi) from the state capital, Shimla.
Kinnaur is bounded by Lahul & Spiti, Kullu, Shimla, state of Uttarakhand while Tibet (China) makes its eastern boundary. The administrative headquarters of the district is at Reckong Peo, situated at an elevation of 2,290 meters. Total area of the district is 6,401 sq. kms.
Kinnaur is known for the mountain peak of Kinner Kailash situated at an altitude of 6,473 meters above mean sea level. The old Hindustan-Tibet Road passes through the Kinnaur valley along the bank of river Sutlej and finally enters Tibet at Shipki La pass. As per one 2016 study Kinnaur had the cleanest air in the country.
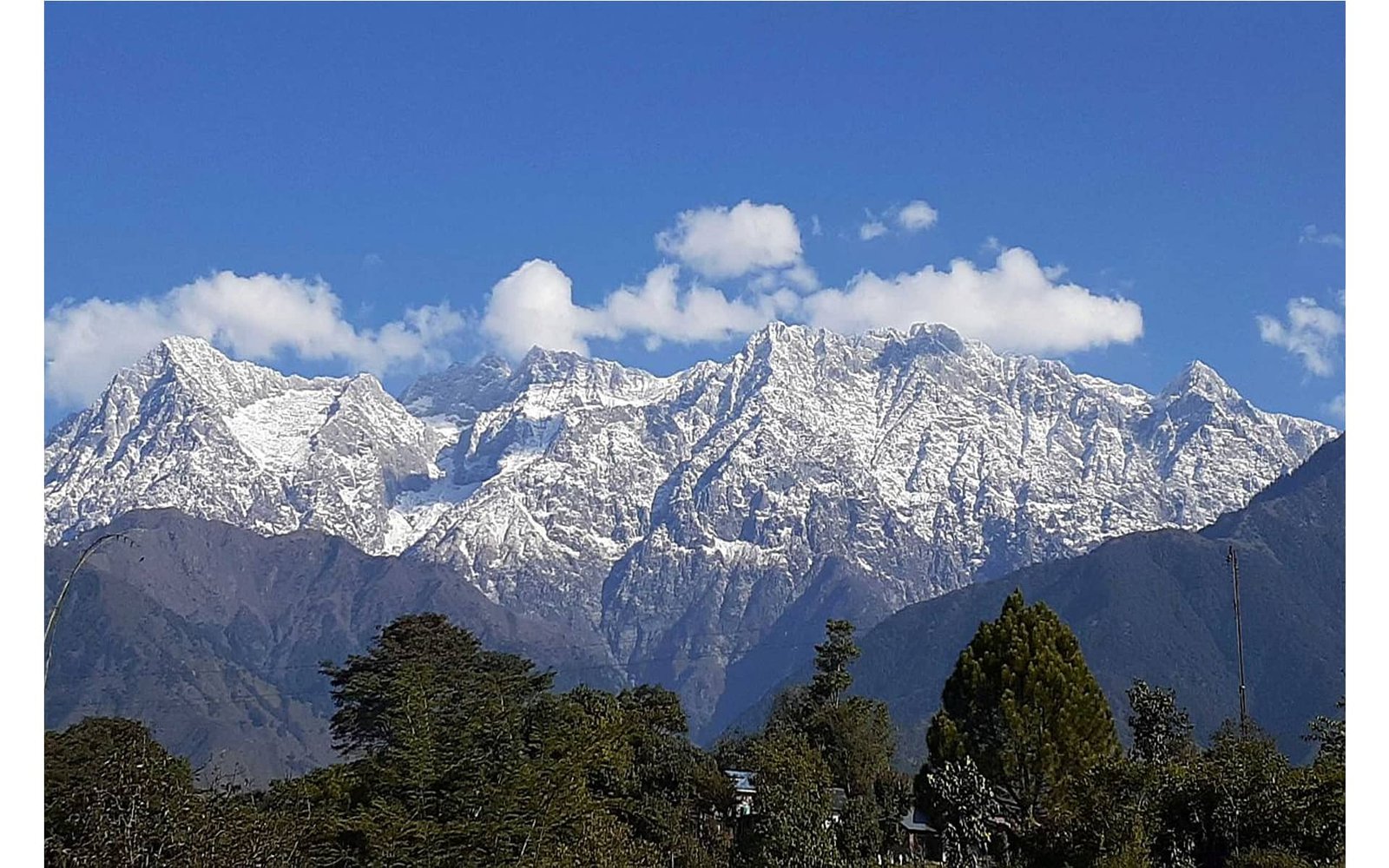

Most of Kinnaur enjoys a temperate climate due to its high elevation, with long winters from October to May, and short summers from June to September. The lower parts of the Sutlej Valley and the Baspa Valley receive monsoon rains. The upper areas of the valleys fall mainly in the rain-shadow area. These areas are arid regions, like the climate of Tibet and Central Asian countries.
Is it a surprise then that a temperate and arid region like Kinnaur will be suited to apple just like father of apple Kazakhstan is?
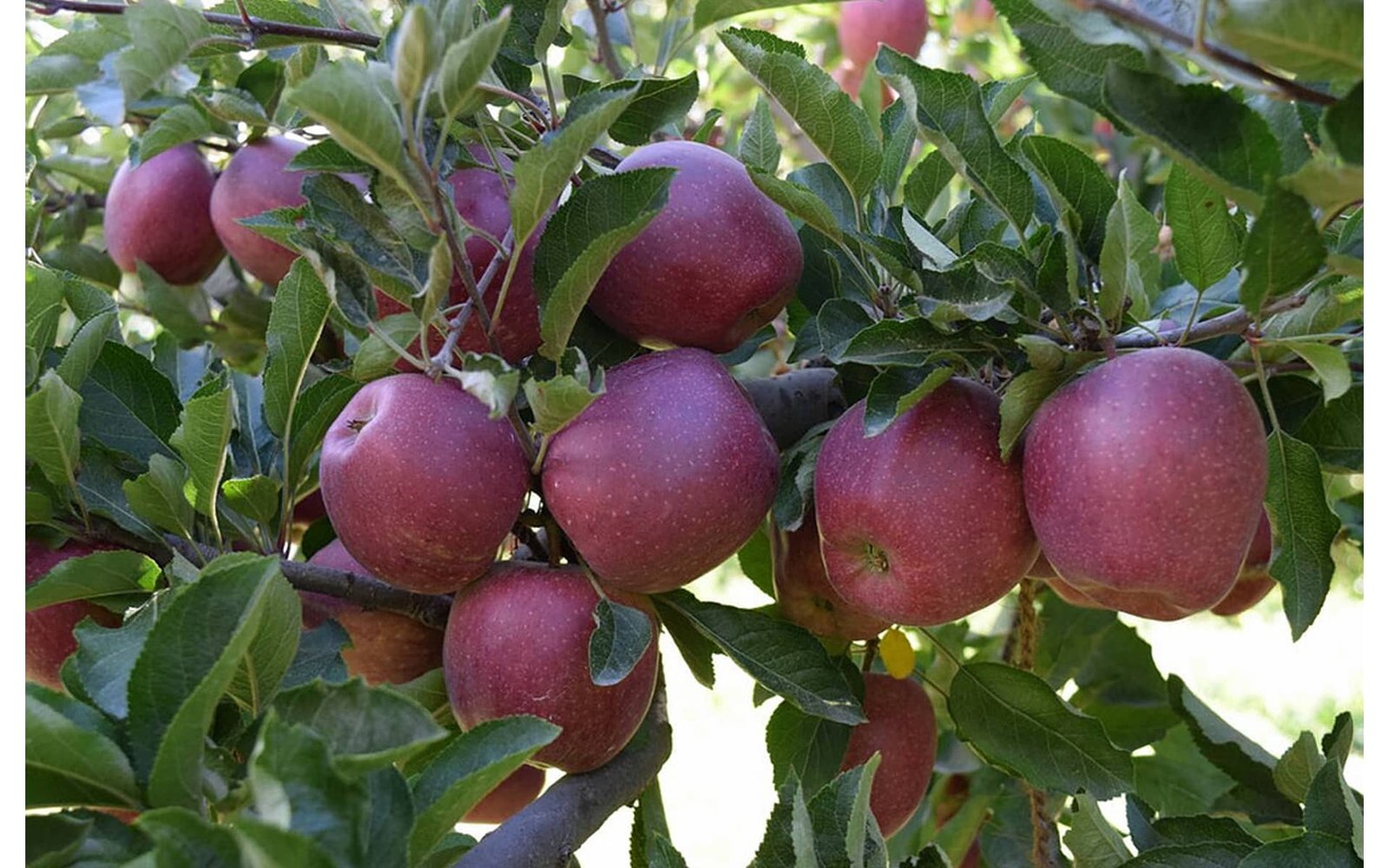

Kinnaur is to apples just like Devgad or Ratnagiri is to Alphonso (Hapus) mangoes. Some of the best quality apples in India is grown in Kinnaur.
The Temperate climate, long winters, Arid conditions, High altitude, pollution free air, and pristine water from glaciers irrigating the orchards, all this adds up to the making of some of the sweetest, juiciest, crunchiest, and long shelf-life apples- the famous Kinnauri Apples.
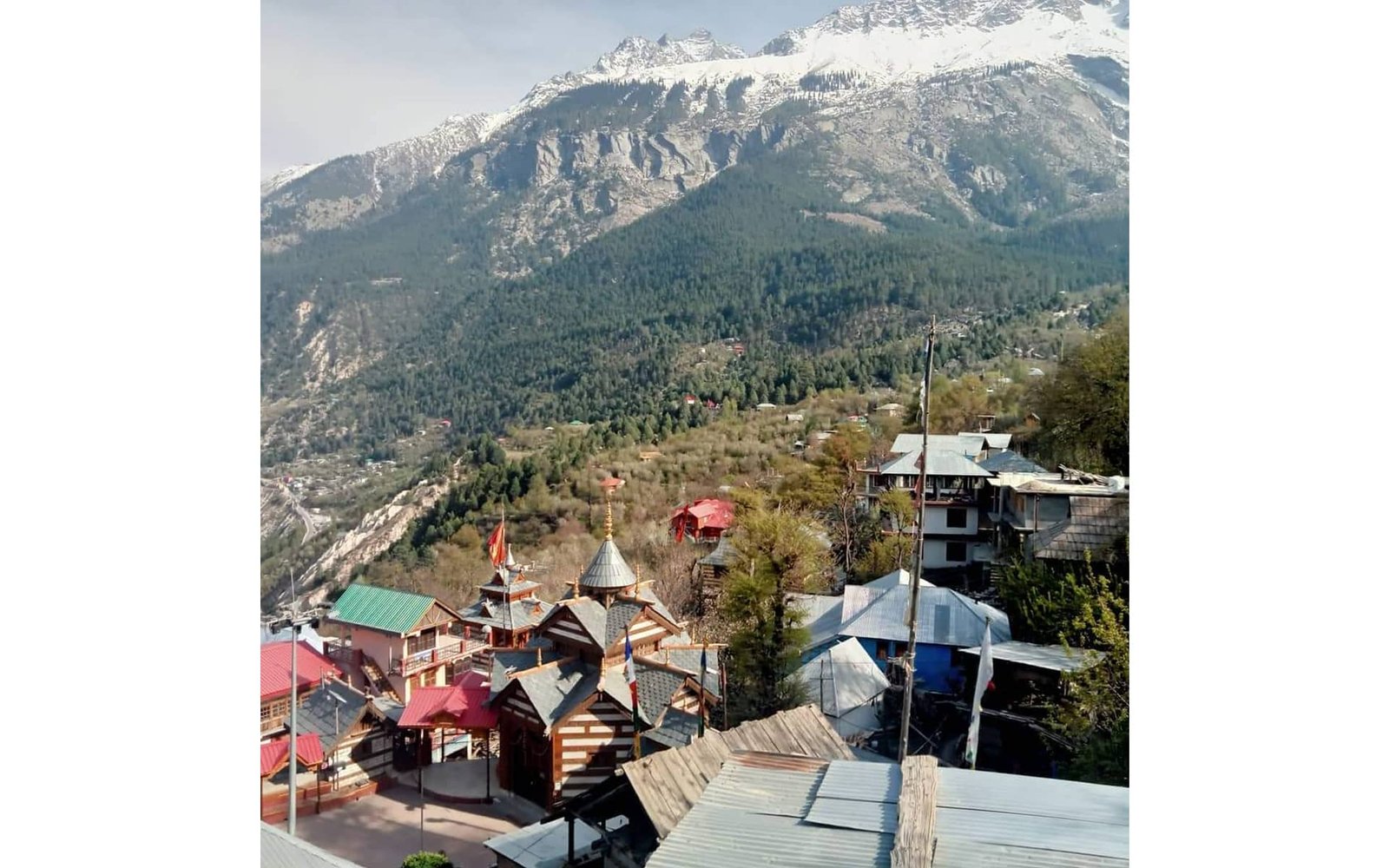

A small village of Kinnaur, Ribba, with a population of just about 1000 people, is nestled at the height of around 3745 meters above the sea (12,286 ft). The village is abundant in Pine nuts and this is how it got its another name, “Rirang”. In the local language, Ri means Pine Nut and Rang means peak.
Dotted with fruit orchards and vineyards, it forms an ideal tourist spot for nature lovers. In addition to best quality Kinnauri Apples, Grape Orchards and Grape Alcohols are the 2 things which are quite popular in this area. The village is bounded by well-known places such as Reckong Peo, Kalpa, Rampur village and Nichar.
Ribba produces close to 3,000 MT of apple annually. For a village of just about 1000 residents it comes to per capita apple production of 3.0 MT! That is a lot of apple.
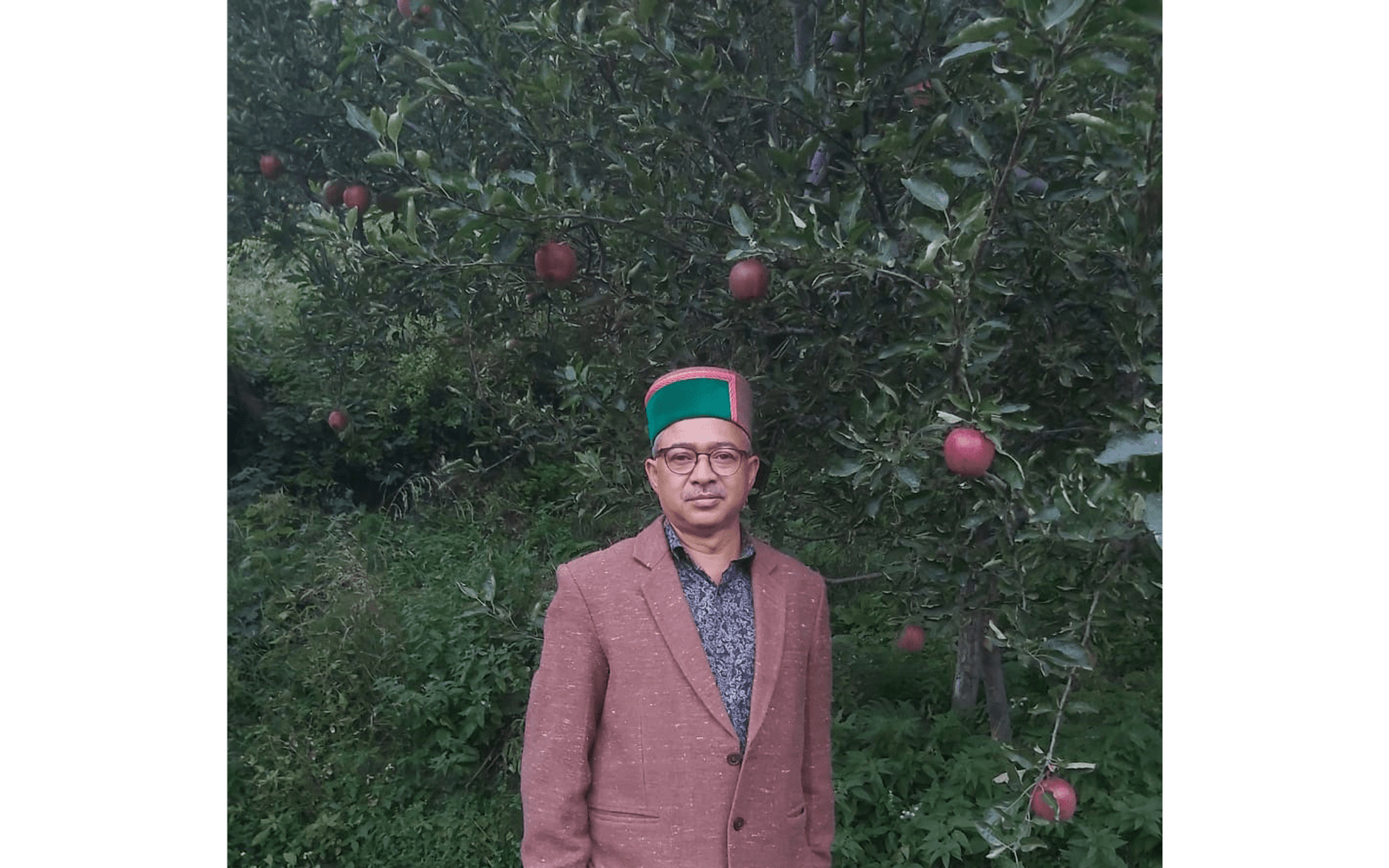
About 2000 kms from Mumbai, in the backdrop of Kinner Kailash range, farmer Negi grows apples in his orchards for more than 20 years now. His family has been doing this for generations.
Ribba is a high altitude village, among the highest growing apples. At the height of 11,000 to 12,500 feet some of the most premium apples are grown- the high altitude delicious Kinnauri apples. Crunchier, juicier, sweeter, having special aroma, and a long shelf life. What more can you ask from an apple?

Hope you liked the fascinating story of apple. You can also be a part of this story!
Join us so that these special kinnauri apples can travel from the orchards in high mountains and into the hands of all apple lovers in mumbai and suburbs.
Directly from the farmers, without the need for any middleman. Thus, giving the much-needed
market access to the farmers for their fresh from farm produce.